Wednesday 3/01
7:00-8:30pm
in WEL 2.224
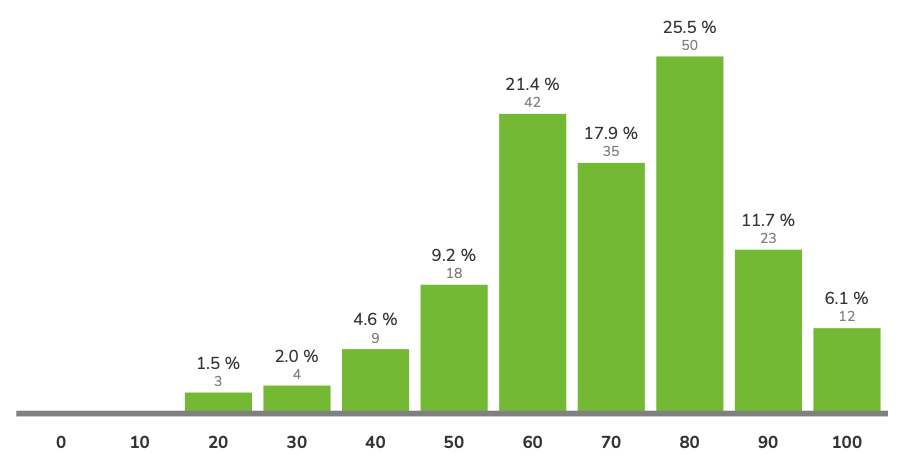
avg = 73.5
🔑 Here are all the KEYS to Exam 2
Students will be able to...
Concepts • Equations - 9 Acid/Base Equilibria
acid / base theory
(Lowry-Bronsted definition)
acid = a proton donor
base = a proton acceptor
Dr. McCord's
Acid/Base Trainer Page
buffer = a solution that resists pH change
water
Kw = [H+][OH-]
pH = -log[H+]
[H+] = 10-pH
pOH = -log[OH-]
[OH-] = 10-pOH
weak acids / weak bases
acid reaction:
HA(aq) ⇌ H+(aq) + A-(aq)
Ka =
[H+][A-]
[HA]
base reaction:
B(aq) (+ H2O) ⇌ OH-(aq) + BH+(aq)
Kb =
[OH-][B+]
[B]
conjugate pairs: Kw = KaKb
buffer composition
a buffer consists of a weak acid AND its conjugate base, or a weak base AND its conjugate acid. BOTH conjugates must be present. You cannot have a buffer with any strong acid and its conjugate or strong base and its conjugate. Buffers MUST come from weak acids and bases.
Henderson Hasselbalch
pH = pKa + log
[base]
[acid]
Here is a very "simple" practice problem set for you to work on and get some experience working through just plain ol' acid/base problems (nothing fancy here). Think of this as a warm up for the other sets.
HTML version (screens): Acid Base Extra Practice
PDF version (print): Acid Base Extra Practice (pdf)
Try your best to complete the practice set. Here are the answers to this set. These are answers only, no explanations or solutions.
Exam 2 · Big-Ass Practice Sets (old Quest HWs)
Some nice old homework sets from Quest. We redid them and called them extra practice a many years ago. Here they are in the 2-column Quest pdf format. Try them all BEFORE you look at the KEY.
Having that déjà vu moment? Some of our old (many actually) get copies over to Canvas.