McClicker Questions for the Semester - if you don't know the answer, go to the class notes for that day and find the McClicker question.
Order is now in REVERSE. Most recent at the top.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
explanation:
In a fractional distillation, which components rise the highest in the fractionating column?
A. Those with the highest boiling points.
B. Those with the lowest boiling points.
C. Those with the highest density.
D. Those with the lowest density.
explanation:
Lowest boiling point components go further up the column before they condense. Higher up the column is lower and lower in temperature.
Which of the following servings has the LOWEST calorie count?
A. Oreo Dream Extreme Cheesecake Slice · Cheesecake Factory
B. Large Peanut Butter Shake · Sonic
explanation:
1620 Calories for the cheesecake - that's about 3 Big Macs. And more impressive is the Sonic shake at 1870 Calories which is about 3.5 Big Macs.Which of the following servings has the LOWEST calorie count?
A. Elvis Presley Memorial Combo · Chuy's
B. Oreo Dream Extreme Cheesecake Slice · Cheesecake Factory
C. Large Peanut Butter Shake · Sonic
explanation:
1280 Calories for all that Tex-Mex.Which of the following servings has the LOWEST calorie count?
A. Elvis Presley Memorial Combo · Chuy's
B. Large Strawberry Shake · Chick-fil-A
C. Oreo Dream Extreme Cheesecake Slice · Cheesecake Factory
D. Large Peanut Butter Shake · Sonic
explanation:
Yes - that shake is 780 Calories.Which of the following servings has the LOWEST calorie count?
A. Large Strawberry Shake · Chick-fil-A
B. Elvis Presley Memorial Combo · Chuy's
C. Big Mac · McDonald's
D. Oreo Dream Extreme Cheesecake Slice · Cheesecake Factory
E. Large Peanut Butter Shake · Sonic
explanation:
Big Mac is "only" 550 Calories.After analyzing this structure, which micronutrient is it?
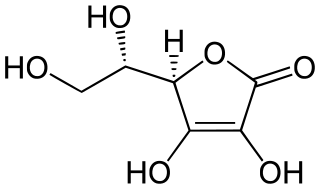
A. vitamin C
B. vitamin D
C. vitamin A
D. mineral Zn
E. vitamin K
explanation:
All the -OH groups indicates that it is a water-soluble vitamin. The only water-soluble vitamin in the choices is vitamin C (aka: ascorbic acid).
In order to make a triglyceride, you have to have ________ to react with ______ fatty acids.
A. glycol ; 3
B. glucose ; 3
C. glycerol ; 3
D. glycol ; 2
E. glycerol ; 2
F. glucose ; 2
explanation:
none
Which one of the following is a monosaccharide?
A. glycogen
B. fructose
C. sucrose
D. starch
E. lactose
F. cellulose
explanation:
Fructose is the only monosaccharide listed.
Which one of the following compounds is a secondary alcohol?
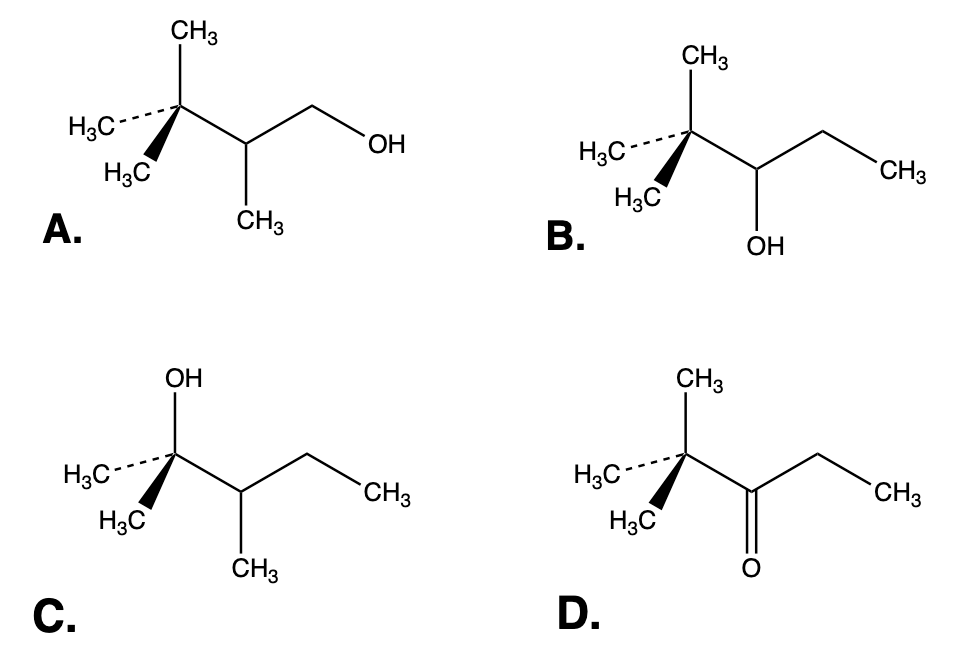
A.
B.
C.
D.
explanation:
In structure B the OH group (what makes an alcohol) is attached to a secondary C (a C attached to 2 other carbons and one H).
I talked about some more polymers today that are not part of the big six. Only one was mentioned as a thermoset type polymer. Which one is it?
A. telfon
B. bakelite
C. nylon
D. cellulose
E. kevlar
explanation:
Bakelite is the only thermoset in the group.
Which one is not an addition polymer?
A. PVC
B. PP
C. PET
D. LDPE
E. HDPE
explanation:
PET is a condensation copolymer, the others are all addition polymers based on ethylene.
Which type of organic reaction is shown below?
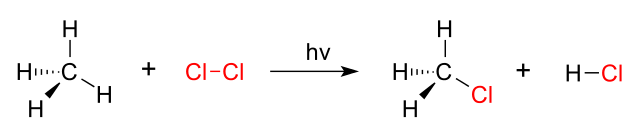
A. elimination
B. substitution
C. addition
D. rearrangement
explanation:
it's a substitutionA. amine
B. ester
C. alcohol
D. ketone
E. ether
explanation:
The added oxygen atom and the fact that it is singly bound between 2 carbons making it an ether.
A. 4-ethyl-3,6-dimethlyheptane
B. 4-ethyl-2,5-dimethlyheptane
C. 2,45-trimethlyheptane
D. 2,5-dimethyl-4-ethlyheptane
E. 3-ethyl-2,6-dimethlyheptane
explanation:
The longest chain is 7 carbons and therefore, heptane. Count to where the branch points are and do it so that the numbers are the smallest possible. This means you start with the upper rightmost carbon. There are then branches at 2, 4, and 5. The groups there are two methyl's and one ethyl. You alphabetize the groups, so ethyl is first so you get 4-ethyl-2,5-dimethylheptane.
A. hexane
B. pentane
C. octane
D. heptane
E. nonane
explanation:
The longest chain is 7 carbons and therefore, heptane.
Consider a AA battery and a D battery - both alkaline cells. The D cell will have ________ potential as the AA cell and will have ___________ capacity.
A. the same; the same
B. a larger; a larger
C. a smaller; a smaller
D. the same; a larger
E. a larger; a smaller
F. a smaller; a larger
explanation:
The chemistry is the same for AA and D cells and the voltage has to be +1.5 V or there 'bouts by design. The D cell is much bigger which means more reactants and products and more capacity.
If you are going to base a useable battery on a voltaic electrochemical cell, to get the most potential (volts), you should make Q as close to _______ as you can get.
A. infinity
B. one
C. zero
explanation:
You'll get higher voltages (more positive) when Q is very very small which means close to zero.
Nernst equation: E = E° - (0.05206/n)log(Q)
What is E° for the cell shown?
A. +0.22 V
B. +0.64 V
C. –0.22 V
D. –0.64 V
E. +0.97 V
explanation:
Subtract +0.20 (the Bi/Bi3+ anode) from –0.44 (the Fe/Fe2+ cathode) to get –0.64 V
What is the standard potential (\(E^\circ\)) for the cell:
\[{\rm Ag~~ \big| ~~AgCl(s) \big| ~~Cl^{-}(aq) ~~\big| \big|~~Fe^{2+}(aq), Fe^{3+}(aq)~~\big| ~~Pt }\]
A. +0.77 V
B. +0.55 V
C. +0.99 V
D. +0.22 V
E. -0.55 V
F. -0.99 V
explanation:
First lookup the standard potential values for each 1/2 reaction from the table. The one on the left is:
AgCl + e- → Ag + Cl- +0.22 V
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ +0.77 V
Now subtract the one on the left side from the right side.
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = E_{\rm right}^\circ - E_{\rm left}^\circ \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +0.77 V - (+0.22 V) \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +0.80 V - 0.22 V \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +0.55 V \)
What is the standard potential (\(E^\circ\)) for the cell:
\[{\rm Cd~~ \big| ~~Cd^{2+}(aq) ~~\big| \big|~~Ag^+(aq)~~\big| ~~Ag }\]
A. +0.40 V
B. +0.80 V
C. +1.20 V
D. -0.80 V
E. -0.40 V
F. -1.20 V
explanation:
First lookup the standard potential values for each 1/2 reaction from the table. You get +0.80 V for the Ag/Ag+ one and –0.40 V for the Cd/Cd2+ one. You will be subtracting the one on the left side because it is the anode and runs as an oxidation (the flipped version of what is in the table).
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = E_{\rm right}^\circ - E_{\rm left}^\circ \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +0.80 V - (-0.40 V) \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +0.80 V + 0.40 V \)
\(E_{\rm cell}^\circ = +1.20 V \)
Potassium dichromate, K2Cr2O7, is an ionic compound with potassium ion (K+) as the cation and the dichromate ion (Cr2O72– ) as the anion.
What is the oxidation number for chromium in dichromate?
explanation:
The oxygens are all –2 and the overall charge is –2 for the dichromate ion. So the math to solve is:
\(2x + 7(-2) = -2\)
\(2x = +12\)
\(x = +6\)
Consider the five changes in oxidation state for five different elements. Which change in state corresponds to a reduction?
A. Fe to Fe2+
B. Cu+ to Cu2+
C. Cl– to Cl
D. Zn2+ to Zn
E. O2– to O–
explanation:
The oxidation number increases for all of these except the Zn one. It starts at +2 and DROPS to 0 (zero). Oxidation number dropping (or decrease) is a reduction.
What is the Ka of an acid that is exactly 10% ionized when mixed at 0.50 M?
A. 1.8×10–5
B. 5.6×10–3
C. 8.2×10–4
D. 1.1×10–1
E. 5.5×10–5
F. 7.2×10–4
explanation:
10% of 0.50 is 0.05. Therefore, both [H+] and [A-] equal 0.05 M. The [HA] is now 0.45 M because it lost 10%. Now substitute those values into the expression:
\(K_{\rm a} = {\rm [H^+][A^-]\over [HA]} = {0.05^2\over 0.45} = 5.6\times 10^{-3}\)
If the pressure of gas CO2 is increased over the surface of fairly neutral water, which of the following will be the result?
A. the pH will rise slightly
B. the pH will stay about the same
C. the pH will drop a bit
explanation:
Higher pressure of CO2 means more will dissolve and that means a more acidic solutin (lower pH)
An unknown concentration of HBr is titrated with 0.0250 M NaOH. 30.0 mL of the acid required 45.0 mL of the base to perfectly neutralize it (the endpoint). What is the concentration of the HBr?
A. 0.0167 M
B. 0.325 M
C. 0.0250 M
D. 0.0375 M
E. 0.0425 M
explanation:
Use formula: MAV1 = MBVB
MA(30) = 0.025(45)
MA = 0.0375 M
A solution with a pH of 5.25 has a hydrogen ion concentration of M.
A. 5.6 × 10–6
B. 1.8 × 105
C. 7.2 × 10–1
D. 2.5 × 10–5
E. 3.3 × 10–6
explanation:
The flipside of the pH formula is [H+] = 10-pH
[H+] = 10-5.25 = 5.6 × 10–6 M
What is the pH of a 0.00055 M HCl solution?
A. 5.50
B. 2.25
C. 7.51
D. 4.33
E. 3.26
F. 3.55
G. 1.79
explanation:
HCl is a strong acid which means that the conc of HCl equals the hydrogen ion (proton) conc
[HCl] = [H+] = 0.00055 M
pH = -log[H+] = -log(0.00055) = 3.25964 = 3.26
8 grams of a solute are added to 56 g of solvent. What is the percent concentration of this solution?
A. 10.0%
B. 14.3%
C. 18.5%
D. 12.5%
E. 15.0%
explanation:
Total mass is 8 + 56 = 64 g. Now use 8/64 to get percentage. 8/64 = 1/8 = 0.125 = 12.5%
Which compound listed below is an ionic compound?
A. H2O
B. CO2
C. MgCl2
explanation:
MgCl2 is a metal cation and non-metal anion which is the definition basically of an ionic compound. The other two are purely covelent compounds (all non-metals).
© 2023 · mccord