Question 11.0 pts
What is the E°cell for
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Ce4+(aq) | Ce3+(aq)
Zn2+ + 2e- Zn E° = -0.76
Ce4+ + e- Ce3+ E° = +1.61
Question 21.0 pts
Question 31.0 pts
What is the standard cell potential of the strongest battery that could be made using these half-reactions?
Br2 + 2e- 2Br- E° = +1.07
Fe3+ + 3e- Fe E° = -0.04
Co3+ + e- Co2+ E° = +1.80
Zn2+ + 2e- Zn E° = -0.76
Question 41.0 pts
What would be the E° of an electrolytic cell made from the half-reactions below?
AgCl(s) + e- Ag(s) + Cl-(aq) E° = +0.22 V
Al3+(aq) + 3e- Al(s) E° = -1.66 V
Question 51.0 pts
Question 61.0 pts
Question 71.0 pts
The galvanic cell below uses the standard half-cells Mg2+ | Mg and Zn2+ | Zn, and a salt bridge containing KCl(aq).
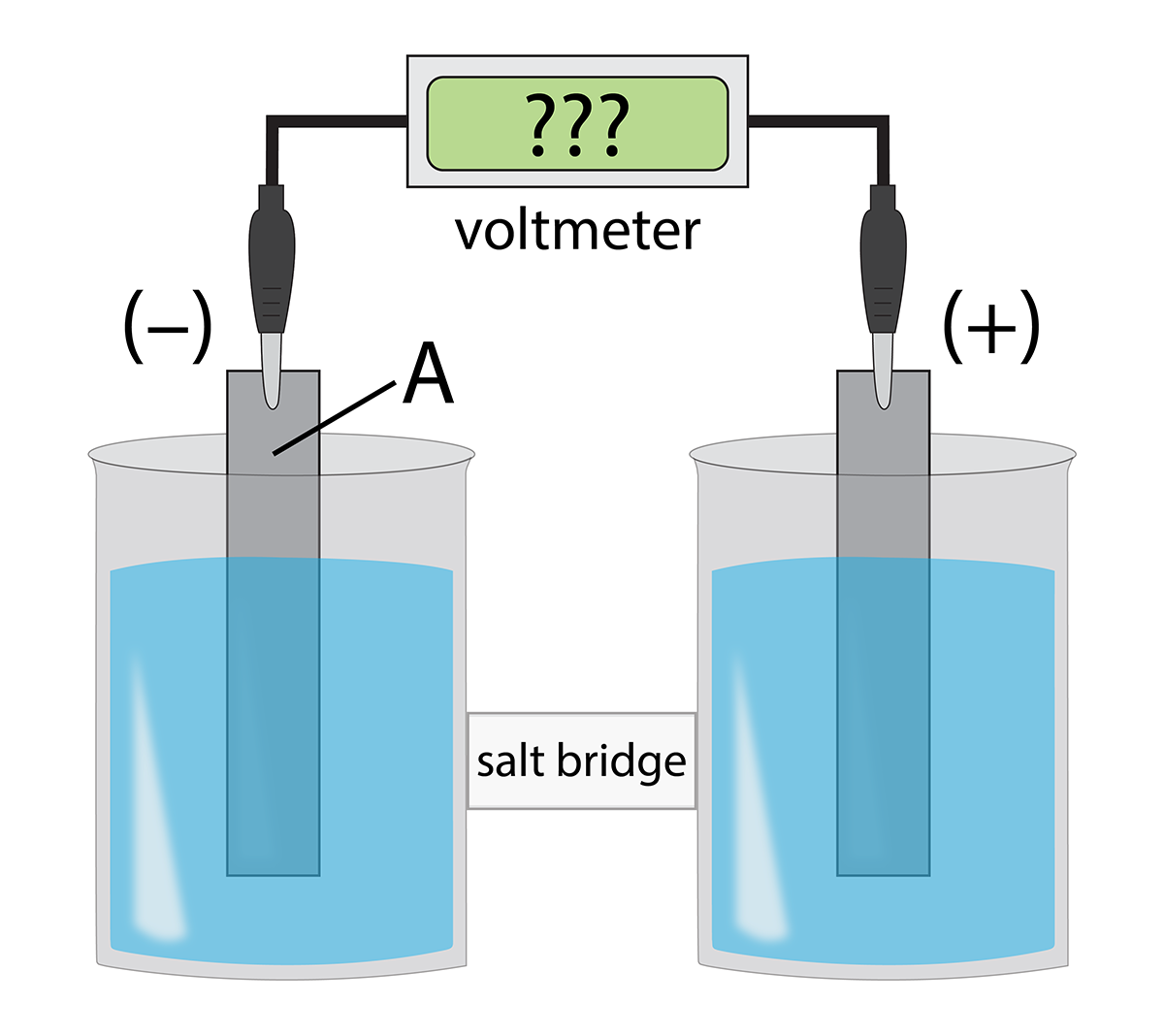
Identify A and write the half-reaction that occurs in that compartment.
Question 81.0 pts
Question 91.0 pts
Question 101.0 pts
How many moles of Cl2(g) are produced by the electrolysis of concentrated sodium chloride if 2.00 A are passed through the solution for 4.00 hours? The equation for this process (the "chloralkali" process) is given below.
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + Cl2(g)
Question 111.0 pts
Question 121.0 pts
Question 131.0 pts
Consider 3 electrolysis experiments:
1. One Faraday of electricity is passed through a solution of AgNO3.
2. Two Faradays of electricity are passed through a solution of Zn(NO3)2.
3. Three Faradays of electricity are passed through a solution of Bi(NO3)3.
Which of the following statements is true?
Question 141.0 pts
What is for the half-reaction below?
ClO3- + 6H+(aq) 0.5Cl2(g) + 3H2O(l) E° = +1.47
Question 151.0 pts
Question 161.0 pts
Consider the cell:
Zn(s) | Zn2+(aq) || Fe2+(aq) | Fe(s)
If run at standard conditions, calculate the value of for the reaction that occurs when current is drawn from this cell.
Question 171.0 pts
Calculate the cell potential for a cell based on the reaction below:
Cu(s) + 2Ag+(aq) Cu2+(aq) + 2Ag(s)
when the concentrations are as follows:
[Ag+] = 0.7 M
[Cu2+] = 0.9 M
(The temperature is 25°C and E° = 0.4624 V.)
Question 181.0 pts
Consider the cell:
Pb(s) | PbSO4(s) | SO42-(aq, 0.60 M) || H+(aq, 0.70 M) | H2(g, 192.5 kPa) | Pt
If E° for the cell is 0.36 V at 25°C, write the Nernst equation for the cell at this temperature.
Question 191.0 pts
A concentration cell consists of the same redox couples at the anode and the cathode and different concentrations of the ions in the respective compartments. Find the unknown concentration for the following cell:
Pb(s) | Pb2+(aq, ?) || Pb2+(aq, 0.1 M) | Pb(s) E = 0.065 V
Question 201.0 pts
What is the ratio of [Co2+] / [Ni2+] when a battery built from the two half-reactions below reaches equilibrium?
Ni2+ Ni E° = -0.25 V
Co2+ Co E° = -0.28 V
Question 211.0 pts
Question 221.0 pts
The standard potential of the cell:
Pb(s) | PbSO4(s) | SO42-(aq) || Pb2+(aq) | Pb(s)
is +0.23 V at 25°C. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the reaction of 1 M Pb2+(aq) with 1 M SO42-(aq).
Question 231.0 pts
The standard voltage of the cell:
Ag(s) | AgBr(s) | Br-(aq) || Ag+(aq) | Ag(s)
is +0.73 V at 25°C. Calculate the equilibrium constant for the cell reaction.
Question 241.0 pts
The equilibrium constant for the reaction below:
2Hg(l) + 2Cl-(aq) + Ni2+(aq) Ni(s) + Hg2Cl2(s)
is 5.6x10-20 at 25°C. Calculate the value of E°cell for this reaction.
Question 251.0 pts
You turn on a flashlight containing brand new NiCad batteries and keep it lit for a minute or two. Which of the following can be considered TRUE regarding the chemical state of these batteries?
I. for the battery reaction is negative.
II. Ecell > 0
III. The batteries are at equilibrium.
IV. Ecell is substantially decreasing during this time.
Question 261.0 pts
Which of the following batteries are rechargeable?
I. Alkaline Battery
II. NiMH Battery
III. Lithium Battery
IV. Lithium Ion Battery
V. Lead-Acid Battery
Question 271.0 pts
Here is the discharge reaction for an alkaline battery:
Zn(s) + 2MnO2(s) + H2O(l)Zn(OH)2(s) + Mn2O3(s)
Which species is reduced as the battery is discharged?
Question 281.0 pts
Question 291.0 pts
The net redox reaction in a fuel cell is given below:
2H2 + O2 H2O
What is the reaction at the anode in a fuel cell?
Question 301.0 pts
CH302 · 50520 Principles of Chemistry II
Spring 2023 · © mccord