Question 11.0 pts
Question 21.0 pts
Question 31.0 pts
Question 41.0 pts
Identify the products of the following chemical reaction:
3LiOH + H3PO4
Question 51.0 pts
Identify the products of the following chemical reaction:
Sr(OH)2 + 2HNO3
Question 61.0 pts
Question 71.0 pts
Question 81.0 pts
Question 91.0 pts
Question 101.0 pts
Question 111.0 pts
Question 121.0 pts
Question 131.0 pts
Question 141.0 pts
Question 151.0 pts
Question 161.0 pts
Question 171.0 pts
Question 181.0 pts
Question 191.0 pts
Question 201.0 pts
Question 211.0 pts
Question 221.0 pts
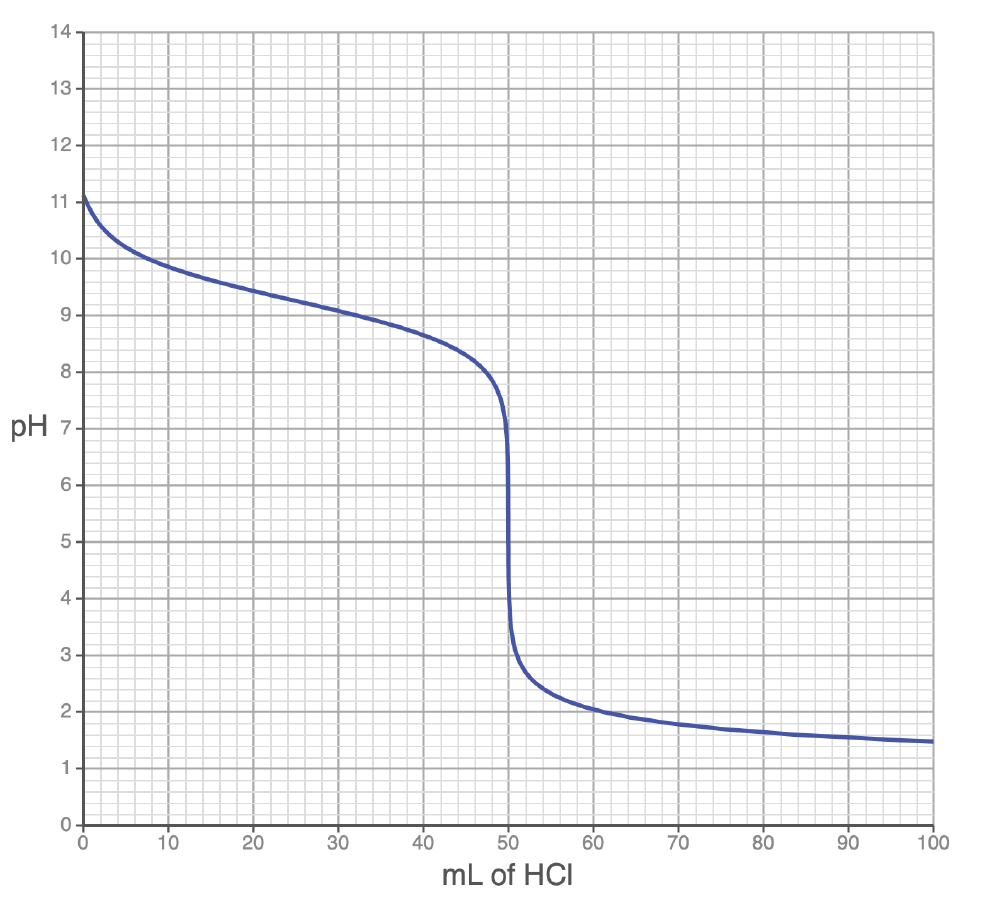
What is the pH at the equivalence point of the titration pictures below?
Question 231.0 pts
Question 241.0 pts
Question 251.0 pts
Question 262.0 pts
Question 271.0 pts
Question 282.0 pts
CH302 · 50520 Principles of Chemistry II
Spring 2023 · © mccord