HW06 - Buffers, Titrations, and Polyprotics
Question 1 1 pts
When an acid and base neutralize each other, the products are generally water and...
- an ion.
- a gel.
- a colloid.
- a salt.
Question 2 1 pts
How many moles of Ca(OH)2 are needed to neutralize three moles of HCl?
- 1
- 1.5
- 3
- 2
Question 3 1 pts
An aqueous solution is prepared with 2 moles of HCl and 1 mole of Ca(OH)2. The resulting solution contains mainly...
- water, Cl- ions, OH- ions, and Ca2+ ions.
- water, Cl- ions, H+ ions, and Ca2+ ions.
- water, Cl- ions, and Ca2+ ions.
- water, Cl- ions, H+ ions, OH- ions, and Ca2+ ions.
Question 4 1 pts
Identify the products of the following chemical reaction:
3LiOH + H3PO4 ⟶
- Li3PO4 + 3H2O
- Li3P + 2H2O + H3O5
- 3H+ + 3O2 + H3Li3
- 3LiH + (OH)3PO4
Question 5 1 pts
Identify the products of the following chemical reaction:
Sr(OH)2 + 2HNO3 ⟶
- Sr(NO2)2 + 2H2O2
- SrNO3 + H2O
- SrH2 + HNO5
- Sr(NO3)2 + 2H2O
Question 6 1 pts
Aqueous ammonia can be used to neutralize sulfuric acid and nitric acid to produce two salts extensively used as fertilizers. They are...
- NH4SO4 and NH4NO3, respectively
- (NH4)2SO4 and NH4NO3, respectively
- NH4SO3 and NH4OH, respetively
- cyanamide and cellulose nitrate, respectively
Question 7 1 pts
Identify the salt that is produced from the acid-base neutralization reaction between potassium hydroxide and acetic acid.
- potassium amide
- potassium cyanide
- potassium acetate
- potassium formate
Question 8 1 pts
What is the pH of an aqueous solution that is 0.018 M C6H5NH2 (Kb = 4.3 × 10-10) and 0.12 M C6H5NH3Cl?
- 2.87
- 4.02
- 3.81
- 4.63
Question 9 1 pts
A buffer solution is made by dissolving 0.45 moles of a weak acid (HA) and 0.33 moles of KOH into 710 mL of solution. What is the pH of this buffer? Ka = 6 × 10-6 for HA.
- 13.23
- 5.22
- 5.66
- 8.34
Question 10 1 pts
Which one of the following combinations is NOT a buffer solution?
- NH3 and (NH4)2SO4
- CH3COOH and NaCH3COO
- HCN and NaCN
- HBr and KBr
Question 11 1 pts
Which of the following mixtures will be a buffer when dissolved in a liter of water?
- 0.2 mol HBr and 0.1 mol NaOH
- 0.3 mol NaCl and 0.3 mol HCl
- 0.2 mol HF and 0.1 mol NaOH
- 0.1 mol Ca(OH)2 and 0.3 mol HI
Question 12 1 pts
What is the pH of a solution which is 0.600 M in dimethylamine ((CH3)2NH) and 0.400 M in dimethylamine hydrochloride ((CH3)2NH2Cl)? Kb for dimethylamine = 7.4 × 10-4
- 11.05
- 10.87
- 10.78
- 11.21
Question 13 1 pts
What would be the final pH if 0.0100 moles of solid NaOH were added to 100mL of a buffer solution containing 0.600 molar formic acid (ionization constant = 1.8 × 10-4) and 0.300 M sodium formate?
- 3.65
- 3.44
- 3.84
- 4.05
Question 14 1 pts
A buffer was prepared by mixing 0.200 moles of ammonia (Kb = 1.8 × 10-5) and 0.200 moles of ammonium chloride to form an aqueous solution with a total volume of 500 mL. 250 mL of the buffer was added to 50.0 mL of 1.00 M HCl. What is the pH of this second solution?
- 8.38
- 8.53
- 8.78
- 8.18
Question 15 1 pts
A solution is 0.30 M in NH3. What concentration of NH4Cl would be required to achieve a buffer solution with a final pH of 9.0? Kb = 1.8 × 10-5 for NH3.
- 0.54 M
- 0.32 M
- 0.45 M
- 0.10 M
Question 16 1 pts
What is the pH at the half-stoichiometric point for the titration of 0.22 M HNO2(aq) with 0.1 M KOH(aq)? For HNO2, Ka = 4.3 × 10-4.
- 2.01
- 7.00
- 2.31
- 3.37
Question 17 1 pts
For the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.020 M aqueous salicylic acid with 0.020 M KOH (aq), calculate the pH after the addition of 55.0 mL of the base. For salicylic acid, pKa = 2.97.
- 10.98
- 11.26
- 7.00
- 11.02
Question 18 1 pts
Consider the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.0200 M HClO(aq) with 0.100 M NaOH(aq). What is the formula of the main species in the solution after the addition of 10.0 mL of base?
- HClO
- NaOH
- ClO2
- ClO-
Question 19 1 pts
50.0 mL of 0.0018 M aniline (a weak base) is titrated with 0.0048 M HNO3. How many mL of the acid are required to reach the equivalence point?
- 4.21 mL
- 18.8 mL
- This is a bad titration as HNO3 is not a strong acid.
- 133 mL
Question 20 1 pts
When we titrate a weak base with a strong acid, the pH at the equivalence point will be...
- It is impossible to know unless we are given the Kb of the weak base.
- pH > 7
- pH = 0
- pH < 7
Question 21 1 pts
What is the pH at the equivalence point in the titration of 10.0 mL of 0.35 M unknown acid HZ with 0.200 M NaOH? Ka = 2.4 × 10-7 for the unknown acid HZ
- 7.00
- 9.86
- 10.1
- 4.14
Question 22 1 pts
What is the pH at the equivalence point of the titration pictures below?
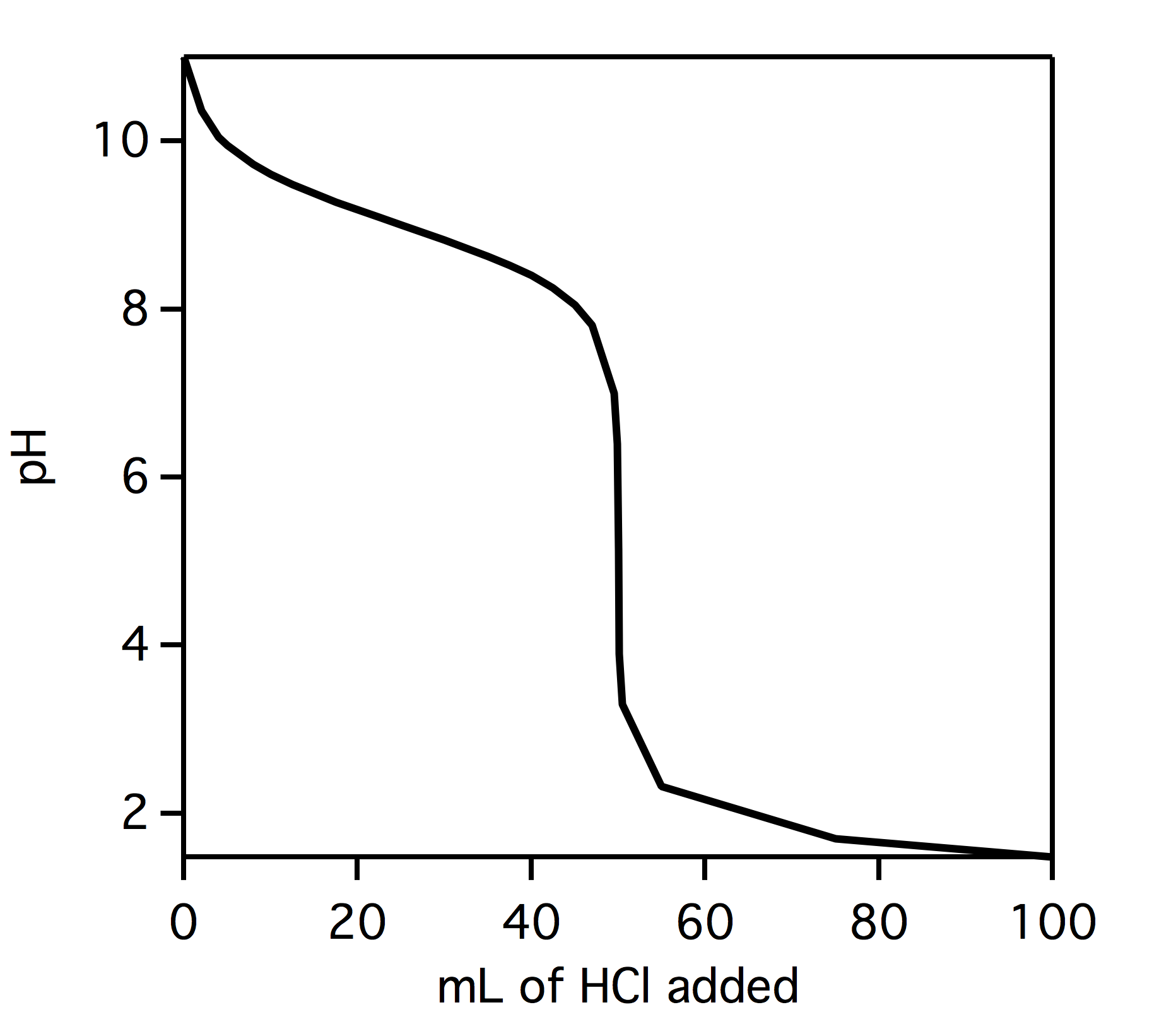
- 8
- 5
- 9
- 2
Question 23 1 pts
Look at the titration diagram in the question above. What type of titration is occurring?
- a weak base titrated with a strong acid
- a strong base titrated with a weak acid
- a strong base titrated with a strong acid
- a weak base titrated with a weak acid
Question 24 1 pts
The acid form of an indicator is yellow and its anion is blue. The Ka of this indicator is 10-5. What will be the approximate pH range over which this indicator changes color?
- 6 < pH < 8
- 4 < pH < 6
- 5 < pH < 7
- 3 < pH < 5
Question 25 1 pts
The unionized form of an acid indicator is yellow and its anion is blue. The Ka of this indicator is 10-5. What will be the color of the indicator in a solution of pH 3?
- orange
- blue
- green
- yellow
Question 26 2 pts
Aspartic acid is a polypeptide side chain found in proteins. The pKa of aspartic acid is 3.86. If this polypeptide were in an aqueous solution with a pH of 7, the side chain would have what charge?
- positive
- negative
- neutral
- there is no way to know
Question 27 1 pts
Blood contains a buffer of carbonic acid (H2CO3) and hydrogen carbonate ion (HCO3–) that keeps the pH at a relatively stable 7.40. What is the ratio of [HCO3–] / [H2CO3] in blood? Ka1 = 4.30 × 10-7 for H2CO3 (Hint: Assume [CO32–] = 0)
- 10.8
- 3.98 x 10-8
- 0.0926
- 1.71 x 10-14
Question 28 2 pts
H2SO4 is a strong acid because the first proton ionizes 100%. The Ka of the second proton is 1.1 × 10-2. What would be the pH of a solution that is 0.100 M H2SO4? Account for the ionization of both protons.
- 0.955
- 0.963
- 2.05
- 1.00